Optical Microscopy Application: Darkfield Illumination
作者: Stephan Briggs
Darkfield illumination is a technique in optical microscopy that eliminates scattered light from the sample image. This yields an image with a dark background around the specimen, and is essentially the complete opposite of the brightfield illumination technique. The primary imaging goal of the darkfield illumination technique is to enhance the contrast of an unstained sample, which is incredibly powerful, yet simple, for live cellular analysis or samples that have not gone through the staining process.
Image Appearance
A typical darkfield illumination image has a white/bright specimen with a dark background and environment filling the image. This is the exact opposite of a brightfield illumination image, and is useful for unstained specimens or images that require increased contrast. The advantage with using darkfield illumination is that unstained specimens can remain alive and vital, whereas their brightfield counterparts must be treated and are no longer active. Also, it is possible to acquire more qualitative results with this technique through live cellular analysis. For additional information on the brightfield technique, please read Optical Microscopy Application: Brightfield Illumination.

Figure 1: Darkfield Illumination Image of Tissue Paper
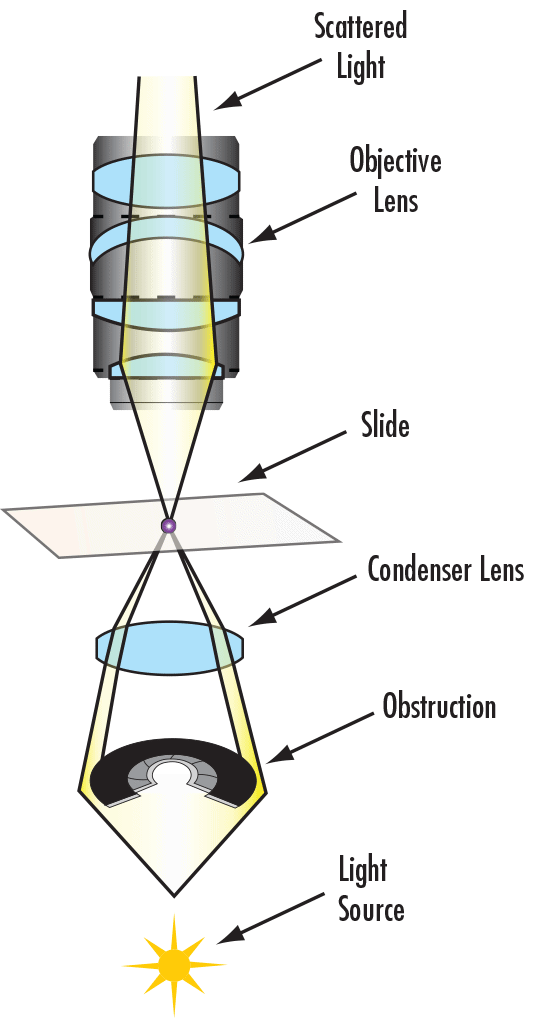
Figure 2: Optical Path for Darkfield Illumination
Technical Details
The light path of the darkfield illumination technique is typically applied to an upright microscope, as seen in Figure 2. The light path consists of three key components.
- Light Source: enters the microscope and hits the dark field patch stop, which is a disc used to block light from entering the condenser and leaves a circular ring of illumination.
- Condenser Lens: collects outer ring of illumination and focuses it on the sample.
- Objective Lens: light hits the sample, and is transmitted or scattered from it. Scattered light enters the objective lens, whereas transmitted light is not collected by the lens. The direct illumination block assists in this step.
Additional optical microscopy applications include brightfield illumination, phase contrast, fluorescence, and differential interference contrast.









































或查看各区域电话
报价工具
只需输入商品编号
Copyright 2023, 爱特蒙特光学(深圳)有限公司。— 广东省深圳市龙华工业东路利金城科技工业园3栋5楼 518109 - 粤ICP备2021068591号